Page 64 - FSTE A5 Handbook
P. 64
Chapter Four
Credit Transfer Practices for
Senior Year Admission
(7) Acceptance policy for upper-division courses
One example in the US is the Ohio Articulation and Transfer Policy which affirms that once
a course has been taken in the sub-degree curriculum, if it is comparable to a course in the
degree programme at the articulating university institutes, the course can also be granted as
degree major credits (Kisker et al., 2012).
The above seven elements provide a common platform for effective articulation by credit
transfer. As the above description pertains only to the US situation, we would like to take a
wider perspective as to how credit transfers are being practised in other overseas countries. To
this end, a summary is provided in Appendix 1 regarding the credit transfer practices in Taiwan,
Singapore, South Korea, the U.S.A., the U.K. and Australia.
Turning back to the local practice, we do not yet have all these elements in place, although
many of them are emerging practices. The following sections will present an in-depth review
on the existing local practices.
Credit Points Required for Graduation by Senior Year Entrants
Senior year entrants refer to students who have completed AD/HD and will be admitted into
the third year of a 4-year undergraduate programme. The intention of having senior year
entrants is to allow greater flexibility in a multi-entry and multi-exit education framework with
greater interflow between self-financing and publicly funded sectors, as well as between sub-
degree and degree sectors in Hong Kong.
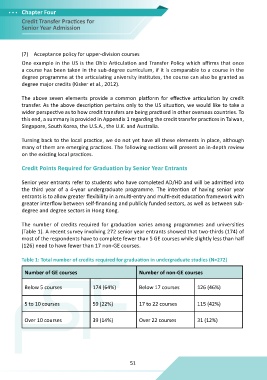
The number of credits required for graduation varies among programmes and universities
(Table 1). A recent survey involving 272 senior year entrants showed that two-thirds (174) of
most of the respondents have to complete fewer than 5 GE courses while slightly less than half
(126) need to have fewer than 17 non-GE courses.
Table 1: Total number of credits required for graduation in undergraduate studies (N=272)
Number of GE courses Number of non-GE courses
Below 5 courses 174 (64%) Below 17 courses 126 (46%)
5 to 10 courses 59 (22%) 17 to 22 courses 115 (42%)
Over 10 courses 39 (14%) Over 22 courses 31 (12%)
51